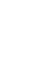Pandemic of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), plastic pollution and climate change are interconnected
Microplastics (MP) is a unique microhabitat for free-living and surface-attached bacterial communities ‘the plastisphere” where they form biofilms facilitating horizontal transfer (HGT ) of antibiotic-resistance genes among bacteria.
Antimicrobial resistome of the plastisphere is plastic resistome. It can spread in aquatic environments under the impacts of climate change on hydrological processes. Temperature changes may prolong the period suitable for cell division and HGT, creating new habitats for bacteria to exist, spread and
develop. Aquatic environments are interfaces for the socio-ecological interactions between humans, animals and the waters containing plastic resistome, facilitating exposure to water-borne AMR.

TULIP creates & advances:
- knowledge on socio-ecological processes and the dynamics of the AMR-MP-climate ecological nexus
- evidence about the linkages to human and animal health
- viable solutions that challenge the status quo and ignite lasting
- change toward health-promoting environments
Novel approaches based on Planetary Health & socio-ecological systems thinking are:
- adaptive geospatial design coupled with hydrological models applied in the selection of sties and frequency of sampling campaigns
- molecular tools to determine dominant MP-associated water-borne AMR and spillback to terrestrial systems
- combining community-based participatory research andintervention science to co-design and evaluate practical solutions, Nature-based Solutions and interventions
- spatio-temporal modelling and machine learning to foster predictive capacity and indicator development
- user-friendly simulation-based decision supporting tools integrated knowledge translation for science-policy translation to guide policies that effectuate systemic transformation and go beyond antibiotic stewardship
- citizen science projects and social innovation to facilitate diffusion of innovation in the community that follows the principles of regenerative economy

Social innovation & Impact
Citizen science: citizen scientists extend the surveillance systems, intervene in the global and local problems of plastic and AMR at the grassroots and policy levels.
Approach: community-based participatory research to understand the needs, underlying community processes and individual behaviour related to plastic and antibiotic pollution and exposure to AMR .
Policy: valuable insights for policies and monitoring initiatives at global, European, national and local levels and evidence on the feasibility of extension AMR monitoring in the environment integrating it with plastic monitoring.
MOOC: a Massive Open Online Course about the AMR-MP-climate change nexus featuring lectures and interviews of the internal and external experts and unique video content.
Social Innovation: events to foster social innovation through conferences and workshops that engage with the communitymembers and provide a forum for the exchange of experience and know-how about launching regenerative economy start-ups, citizen science projects and community collaborative actions.
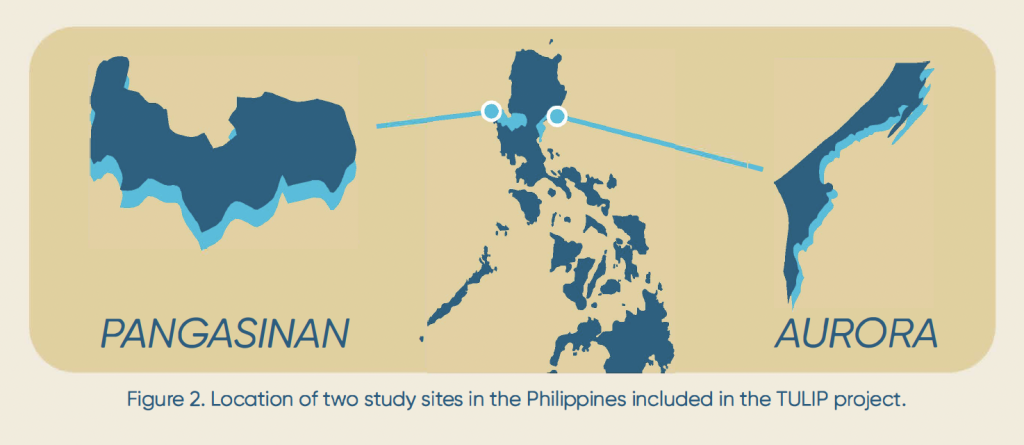
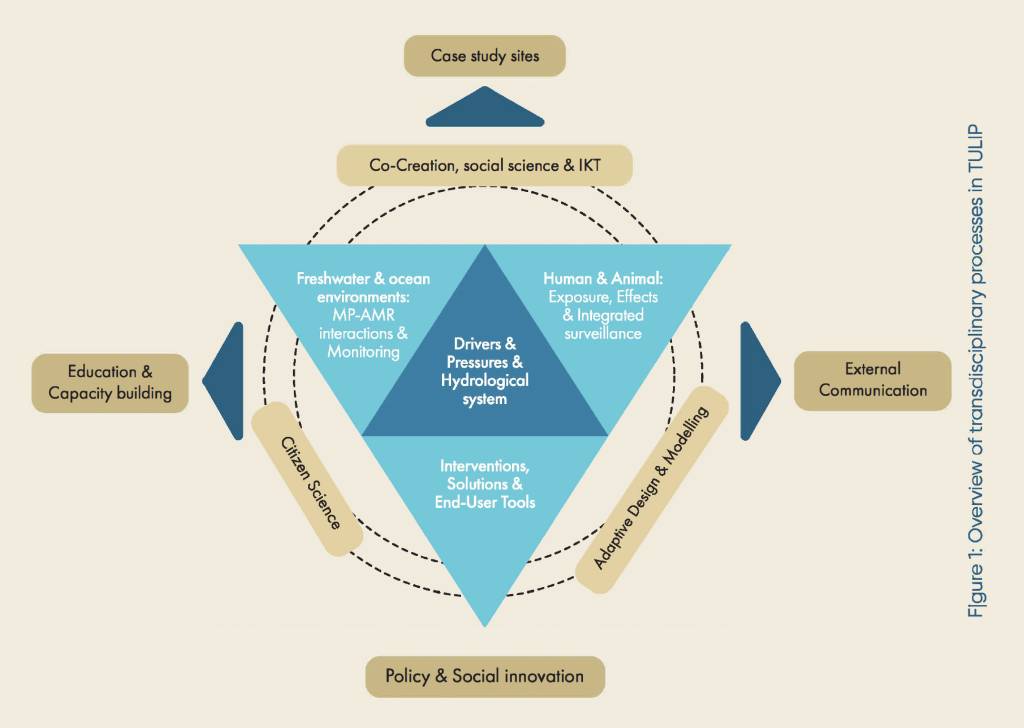
Study areas in the Philippines
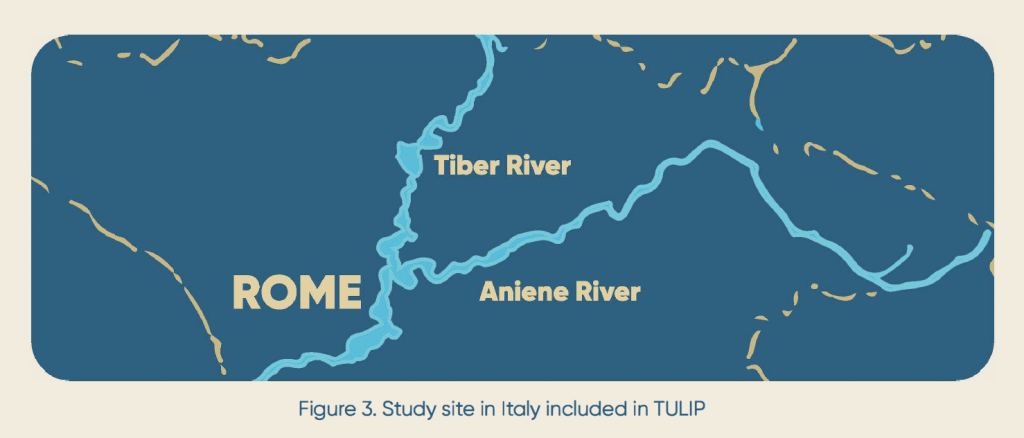
Study areas in Italy
“TULIP”
Research
“TULIP”
Solutions
“TULP”
Knowledge Exchange